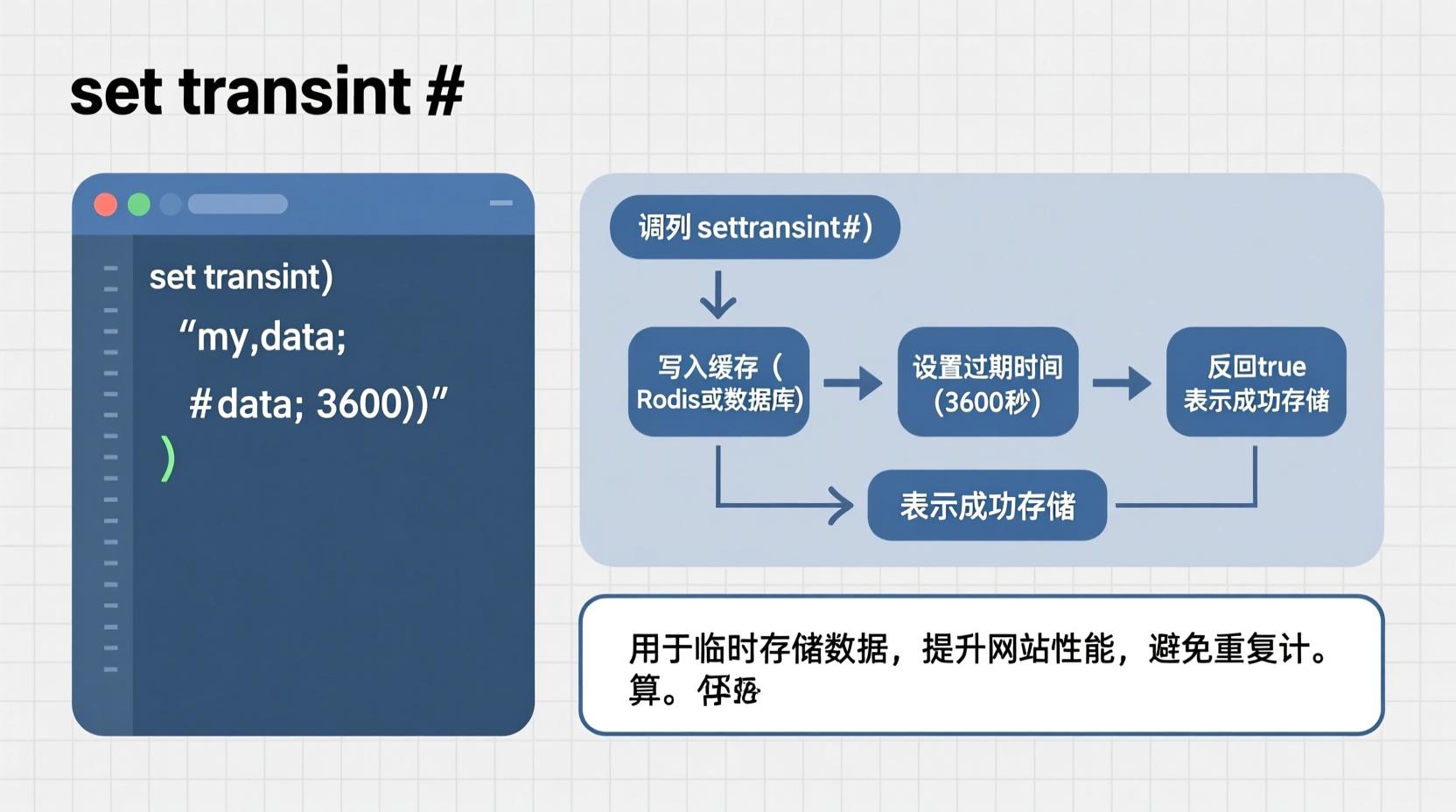
 set_transient()
set_transient()transient API 的一部分,常用于缓存数据库查询、API 响应或其他计算密集型操作的结果。
一、基本概念
1. 什么是 Transient?
Transient 是 WordPress 中的一种缓存机制,类似于 Redis 或 Memcached 的键值对缓存,但它是基于文件或数据库(取决于 WordPress 配置)的。它适用于短期缓存的数据,比如:
- API 请求结果
- 复杂查询的结果
- 页面生成的输出
- 一些不经常变化但需要快速访问的数据
2. 与 set_transient() 相关的函数
| 函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
set_transient($key, $value, $expiration) |
设置一个 transient |
get_transient($key) |
获取一个 transient |
delete_transient($key) |
删除一个 transient |
transient_exists($key) |
检查 transient 是否存在 |
二、set_transient() 函数详解
语法
set_transient( $transient, $value, $expiration );参数说明
| 参数 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
$transient |
string | 是 | transient 的名称(键),通常使用唯一标识符,如 'my_cache_key' |
$value |
mixed | 是 | 要存储的值,可以是字符串、数组、对象等 |
$expiration |
int | 否 | 过期时间(秒),0 表示永不过期(不推荐) |
注意:WordPress 5.7 及以上版本中,
$expiration为0时,transient 不会过期。建议使用60 * 60 * 24等表示天数。
三、使用示例
示例 1:缓存 API 数据
function get_api_data() {
$cache_key = 'api_data_cache';
$data = get_transient( $cache_key );
if ( false === $data ) {
// 如果缓存不存在,从 API 获取数据
$response = wp_remote_get( 'https://api.example.com/data' );
$body = json_decode( wp_remote_retrieve_body( $response ), true );
$data = $body['data'];
// 设置缓存,有效期为 1 小时(3600 秒)
set_transient( $cache_key, $data, 3600 );
}
return $data;
}示例 2:缓存数据库查询结果
function get_user_posts( $user_id ) {
$cache_key = 'user_posts_' . $user_id;
$posts = get_transient( $cache_key );
if ( false === $posts ) {
global $wpdb;
$posts = $wpdb->get_results( $wpdb->prepare(
"SELECT * FROM {$wpdb->prefix}posts WHERE post_author = %d",
$user_id
), OBJECT );
set_transient( $cache_key, $posts, 60 * 60 * 24 ); // 1天
}
return $posts;
}四、注意事项
- Transients 依赖于缓存系统:
- 默认情况下,WordPress 使用文件缓存(
wp-content/cache/)。 - 如果你使用了缓存插件(如 W3 Total Cache、WP Super Cache),可能会影响 transients 的行为。
- 默认情况下,WordPress 使用文件缓存(
- 不要用作持久化存储:
- Transients 是临时数据,不能替代数据库或选项(option)存储。
- 命名规范:
- 建议使用有意义的 key 名称,避免冲突,例如:
'myplugin_cache_123'。
- 建议使用有意义的 key 名称,避免冲突,例如:
- 过期时间合理设置:
- 过期时间太短可能导致频繁重新获取数据,影响性能;
- 太长则可能缓存过时数据。
五、删除 Transient
delete_transient( 'api_data_cache' );六、检查 Transient 是否存在
if ( transient_exists( 'api_data_cache' ) ) {
// 存在
} else {
// 不存在
}七、总结
| 功能 | 用途 |
|---|---|
set_transient() |
缓存临时数据 |
get_transient() |
获取缓存数据 |
delete_transient() |
清除缓存 |
transient_exists() |
判断是否存在缓存 |
如果你有具体的应用场景(比如缓存某个 API 接口、页面内容、数据库查询等),我可以提供更具体的代码示例。
是否需要我帮你写一个完整的例子?




0 条评论